Welcome to the forums at seaphages.org. Please feel free to ask any questions related to the SEA-PHAGES program. Any logged-in user may post new topics and reply to existing topics. If you'd like to see a new forum created, please contact us using our form or email us at info@seaphages.org.
Recent Activity
Fin anti-sigmaF factor
| Link to this post | posted 18 Apr, 2025 02:55 | |
|---|---|
|
|
We would like to propose the function "Fin anti-sigmaF factor" should be added to the Functional Assignment list. Zippen_60 (43340 bp- 43552 bp) may be a "Fin anti-sigmaF factor" Sequence is: MAQREVITFICDNCGGEDDLKEGQILPTGWMEILFTENSQANEPVQTCQLCTDAVAKALAERRGDIAPSK Currently 47 members of this Pham from a variety of clusters. Some annotated as "DNA binding protein" Support for the function: 1. Two HHPred hits, greater than 96% probability and high coverage, to "Anti-sigma-F-factor" (see attached image or go to the HHPred Job https://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/jobs/1090560 Hit 1: PF10955.11 - http://pfam-legacy.xfam.org/family/PF10955.11 Hit 2: PDB 5MSL - https://www.rcsb.org/structure/5MSL 2. Protein has two CXXC motifs spaced about 35 resides apart. These conserved cysteine pairs are critical for coordinating a Zn²⁺ ion in anti-sigma factor domains which bind Zinc and is similar to the zinc-binding anti-sigma factors Fin and CsfB from Bacillus subtilis (see the paper doi:10.1111/mmi.13724) 3. MSA alignment for the pham shows that two conserved CXXC motifs (see attached image) 4. Alphafold3 predictions of Fin and Zippen_60 are somewhat similar, and predicts Zn binding by the four cysteines in Zippen_60 and strong probability for dimerization, similar to Fin. See Attached images. |
| Link to this post | posted 18 Apr, 2025 21:37 | |
|---|---|
|
|
You posted really good evidence in support of the presence of zinc finger domains which are often part of DNA binding domains. However in the Mol Microbiol. 2017 Aug;105(4) paper they note that the Fin protein actually has a protein:protein interaction with RNA polymerase. I only did a quick scan of the figures but it appars they did nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shift analysis of fin in the presence of B' to look for evidence for which amino acids are involved in this protein protein interaction. See fig 5C. In there it looks like the residues that are the most perturbed and therefor the most likely to be critical for binding are Gly 15 and Glu 45. So the question is are those residues conserved? if so then you might have an argument for an annotation but just having a zinc finger motif means the only annotation justifieed is "zinc finger doamin" and we usually do not annotate just domain. I think is especially valid in this case as most people, including myself, think of zinc finder domains as DNA binding domains but this paper say that Fin is a RNA polymerase binding not DNA. binding. So I would stick with NKF |

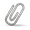 1.32Mb
1.32Mb